India Reveals Six Water Infrastructure Projects in Response to the Indus Treaty Suspension
After the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) was suspended India made a significant change to its water management plan. The nation has announced six new water infrastructure projects aimed at maximizing the use of its rivers especially those that flow from the Indus basin in a move that demonstrates both foresight and resilience. India has also started reservoir flushing operations which represents a change in the country’s strategy for water use and conservation.
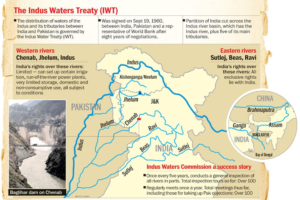
Context: The Suspension of the Indus Waters Treaty

The World Bank mediated the 1960 signing of the Indus Waters Treaty between India and Pakistan which regulated the use of six rivers in the Indus basin. The treaty gave Pakistan rights to the western rivers the Indus Jhelum and Chenab while giving India control over the eastern rivers the Ravi Beas and Sutlej. India was granted limited access to the western rivers for the production of hydropower for domestic agricultural and non-consumptive purposes.
However India chose to halt the agreement due to rising geopolitical tensions between the two neighbors and concerns about Pakistan’s purported abuse of treaty provisions. Though contentious this action has been seen as a reorientation of India’s water policy guaranteeing that its own interests are given precedence in the administration of these vital water resources.
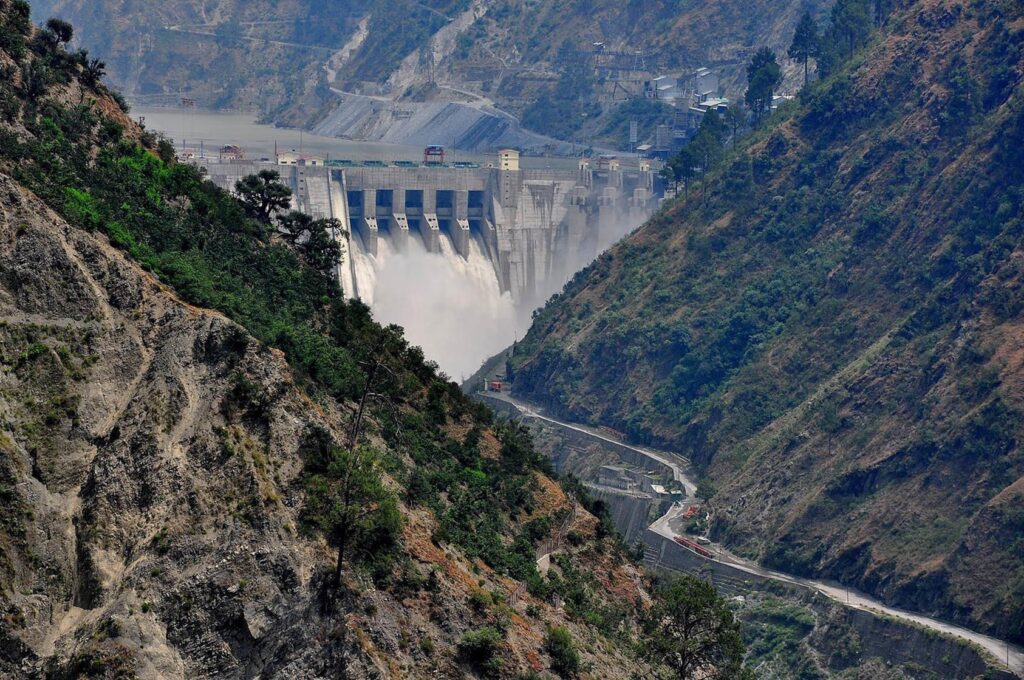
A Strategic Choice for Water Management: Reservoir Flushing

A crucial part of maintaining water infrastructure is reservoir flushing which removes sediment accumulation from reservoirs to increase their effectiveness. India has started flushing operations to guarantee the best possible performance of its water storage facilities since the Indus Treaty was suspended. It is anticipated that this action will maintain sustainable irrigation methods throughout northern India improve water flow and stop silt buildup.
IOC Shares Surge 4%
Long-term advantages of flushing reservoirs can be substantial and include:

- increased capacity to store water through the reduction of sediment deposits.
- increased production of hydroelectric power while preserving turbine efficiency.
- improved irrigation techniques for farmers who depend on these reservoirs for their water supply.
The Six New Projects for Water Infrastructure

In addition to regaining control India’s decision to halt the Indus Treaty is an attempt to secure its water supply for the future. Six new water infrastructure projects have been announced by the government in response. It is anticipated that these projects will increase India’s capacity to utilize its river systems for energy production domestic use and agriculture.
Among the initiatives are:
- building new reservoirs and dams to effectively store and control river flow.
- enlarged irrigation systems to aid northern Indian farmers.
- Hydroelectric power plants have been upgraded to maximize the production of renewable energy.
- projects aimed at diverting water to areas that are experiencing a shortage.
- enhanced flood control systems to safeguard communities at risk.
- Improved water filtration systems for safe and easily available drinking water.
In addition to making efficient use of its river resources, these projects support India’s larger goal of sustainable water management, which includes getting ready for future issues brought on by population growth and climate change.
Geopolitical Consequences
India-Pakistan relations will probably be significantly impacted by the treaty’s suspension and the ensuing infrastructure projects. Any interruption in water flow could lead to tensions because Pakistan is heavily dependent on the rivers of the Indus basin. Nonetheless India argues that these actions are perfectly within its legal rights under international law because the terms of the treaty permit India to make efficient use of its portion of the rivers.
Furthermore, India’s action is indicative of a broader geopolitical shift that prioritizes independence and strategic preparation. India is reaffirming its commitment to environmental sustainability and claiming control over its natural resources by funding new water projects.
Conclusion: India’s Water Management Enters a New Era
An important shift in India’s strategy for managing its water resources was brought about by the suspension of the Indus Waters Treaty. The nation’s dedication to maximizing its river systems while guaranteeing long-term sustainability is demonstrated by the flushing of reservoirs and the start of six new water projects.
Given the growing risks that climate change poses to the world’s water security India’s proactive actions may serve as a template for other countries dealing with comparable issues. The accomplishment of these projects will be closely monitored as the nation pursues its ambitious plans both for their overall effects on regional water governance and for their effects on India’s infrastructure.
India has a clear position on managing its water resources: sustainability self-reliance and strategic use. These changes have the potential to change South Asia’s water security environment in the years to come.





